Nanoplastics | How Plastic Polymer Nanoparticles Negatively Affect The Immune System

Ana Maria Mihalcea, MD, PhD | substack.com/@anamihalceamdphd
New Study Shows Significant Impact Of Nanoplastics (NP)On Immune Function Causing Cell Toxicity, Inflammation, Cancer And Death Of Red Blood Cells. NP Accumulate In Organs.
A new study published in Advanced materials showed significant effects of nanoplastics on immune system function - upregulation of inflammatory response.
Inflammation drives all diseases of aging, causes acidity in the body and lowers cellular electrical voltage. If we looks at the body from and electro physiology perspective, this study confirms what we have been seeing in the human population - an accelerated aging process and immune dysfunction, leading to accelerated cardiovascular, endocrine and neurological problems and the rise of turbo cancers.
“These results demonstrate that NPs can interact with, interfere with, and translocate into several immune cell subpopulations after exposure. In vivo distribution experiments in mice further confirmed their accumulation in immune cells within the liver, blood, and spleen, particularly in monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells.”
Abstract
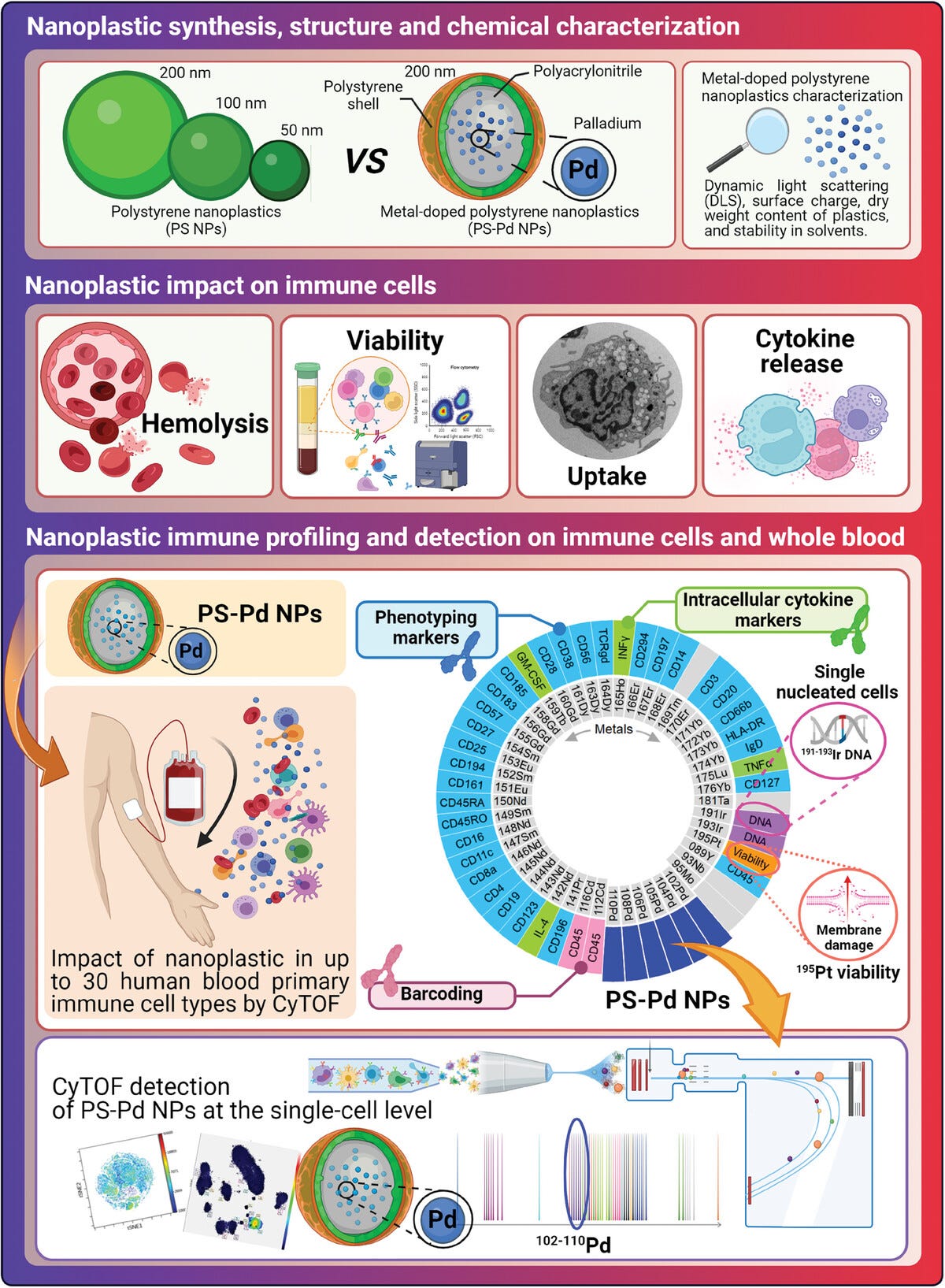
The increasing exposure to nanoplastics (NPs) raises significant concerns for human health, primarily due to their potential bioaccumulative properties. While NPs have recently been detected in human blood, their interactions with specific immune cell subtypes and their impact on immune regulation remain unclear. In this proof-of-concept study, model palladium-doped polystyrene NPs (PS-Pd NPs) are utilized to enable single-cell mass cytometry (CyTOF) detection. The size-dependent impact of carboxylate polystyrene NPs (50–200 nm) is investigated across 15 primary immune cell subpopulations using CyTOF. By taking advantage of Pd-doping for detecting PS-Pd NPs, this work evaluates their impact on human immune-cells at the single-cell level following blood exposure. This work traces PS-Pd NPs in 37 primary immune-cell subpopulations from human blood, quantifying the palladium atom count per cell by CyTOF while simultaneously assessing the impact of PS-Pd NPs on cell viability, functionality, and uptake. These results demonstrate that NPs can interact with, interfere with, and translocate into several immune cell subpopulations after exposure. In vivo distribution experiments in mice further confirmed their accumulation in immune cells within the liver, blood, and spleen, particularly in monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. These findings provide valuable insights into the impact of NPs on human health.
The article cites a study from 2022 finding plastic nanoparticles in human blood. Surprise! After the COVID19 bioweapon rollout we have found polymer hydrogel plastics in everyone’s blood.
Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood
Plastic particles are ubiquitous pollutants in the living environment and food chain but no study to date has reported on the internal exposure of plastic particles in human blood. This study’s goal was to develop a robust and sensitive sampling and analytical method with double shot pyrolysis - gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and apply it to measure plastic particles ≥700 nm in human whole blood from 22 healthy volunteers. Four high production volume polymers applied in plastic were identified and quantified for the first time in blood. Polyethylene terephthalate, polyethylene and polymers of styrene (a sum parameter of polystyrene, expanded polystyrene, acetonitrile butadiene styrene etc.) were the most widely encountered, followed by poly(methyl methacrylate). Polypropylene was analysed but values were under the limits of quantification. In this study of a small set of donors, the mean of the sum quantifiable concentration of plastic particles in blood was 1.6 µg/ml, showing a first measurement of the mass concentration of the polymeric component of plastic in human blood. This pioneering human biomonitoring study demonstrated that plastic particles are bioavailable for uptake into the human bloodstream. An understanding of the exposure of these substances in humans and the associated hazard of such exposure is needed to determine whether or not plastic particle exposure is a public health risk.
Just reminding everyone of the stealth nanoparticles in the Moderna patent that contains polyethylene, polystyrene, polymethacrylate:

The scientists analyzed effects on 15 different immune system cells and found inflammation was triggered as well as immune system dysfunction - inhibiting the ABILITY TO FIGHT PATHOGENS.
We used carboxylate polystyrene nanoparticles (PS NPs), with diameters ranging from 50 to 200 nm, to evaluate the size-dependent impact of NPs on fifteen primary human immune cells. Moreover, we studied their effects after blood exposure by single-cell mass cytometry (CyTOF),[52] a crucial and innovative technology to decipher the biological impact of various agents in depth.[
Following human exposure, NPs could affect immune cells by triggering an inflammatory response, leading to chronic inflammation and immune dysregulation.[43] Additionally, NPs may interfere with immune cell activities such as phagocytosis and cytokine release,[59] compromising the ability of the immune system to fight pathogens. It has been demonstrated that NP size can play an important role in determining their toxic effects.
Size matters, the larger they are the more toxic. Now remember they only looked at the nanoscale - I see polymer filaments that are hundreds of times larger than a red blood cell ( diameter 5 micrometers). What is their relative toxicity?
Overall, our data demonstrate that larger PS NPs (200 nm) are more effective in inducing cytokine production and immune cell activation, suggesting a role of particle size in their ability to affect immune cell functions, in particular in T cells and monocytes. The larger the NP, the greater the surface area, which may be conducive to increased cytokine production, suggesting that size is a critical factor in their immune impact
The Nanoparticles induce red blood cell death called hemolysis - we have seen that in many experiments and I have shown that in live blood analysis. Remember when I showed how the nano and microbots in dental anestethics kill red blood cells in minutes
This is what the study showed:
To evaluate the potential hemolytic activity of NPs, human red blood cells were exposed to 50 µg mL−1 of PS NPs or PS-Pd NPs for 1 and 24 h (Figure S7d, Supporting Information). PS-Pd NPs induced hemolysis only after 24 h, while we observed no significant release of hemoglobin caused by PS NPs.
In this part of the study you can see that there are many different pathways of how these nanoparticles are causing inflammation as well as cancer like leukemia. This would explain why I and other doctors see turbo cancers in the unvaccinated as well now, since the plastic nanoparticles are cancerogenic via multiple pathways.
To this extent, the modulation of several ribosomal genes and proteins also suggests increased cell stress and possibly cell death.[81] This aligns with existing literature where treatments that induce oxidative stress have been shown to upregulate similar protective genes and proteins.[82] Intriguingly, among the top upregulated pathways identified by gene expression analysis, we found the AIM2 inflammasome pathway (Figure 3c). The AIM2 inflammasome is responsible for sensing self and non-self DNA in the cytosol. This detection initiates inflammasome assembly and IL-1β release, promoting inflammation.[83] Together with the previous ROS data, this suggests that PS NP may induce damage to the mitochondria, leading to DNA release and inflammasome activation. At the same time, we found the downregulation of TNFR1-mediated ceramide production and IL-38 signaling, indicating suppression of anti-inflammatory mechanisms, potentially leading to an overall increase in inflammation and cytokine production.[84, 85] The upregulation of the SMAC-XIAP-regulated apoptotic response pathway suggests an increase in mediated cell death, as SMAC (Second Mitochondria-derived Activator of Caspases) promotes apoptosis by inhibiting XIAP (X-linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein), thereby facilitating caspase activation which is also needed for the inflammasome pathway activation.[86] Similarly, the modulation of the RUNX1 in the differentiation of myeloid cells pathway is known to promote inflammation and an improper monocyte maturation that may lead to Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML).[87] The proteomic analysis confirmed the regulation of similar pathways, including the RUNX1-regulated transcription of genes involved in the interleukin signaling pathway (Figure 3d). The upregulation of apoptosome activity is a crucial complex in the intrinsic apoptosis pathway.[87] The upregulation of pathways associated with defective HEXA (HEXA gene mutations leading to Tay-Sachs disease) causing GM2 gangliosidosis also implies increased cellular stress.[88] Conversely, the downregulation of the Nonsense-Mediated Decay (NMD) pathway, which usually degrades faulty mRNA transcripts, may result in the accumulation of defective proteins, contributing to cellular stress and apoptosis.[89] Finally, the modulation of amine oxidation pathways and aldehyde generation, such as monoamine oxidases, MAOA, and MAOB, further highlights that PS NPs induced apoptosis and ROS formation through enhanced cellular stress mechanisms (Figure 3d). These data collectively suggest that PS NPs significantly impact monocytes by inducing mitochondrial damage, triggering inflammasome activation, promoting apoptosis, and enhancing cellular stress, leading to a complex pro-inflammatory response.
Summary:
There is clear evidence that plastic polymer nanoparticle affect the immune system in every way imaginable in and adverse way. Inflammation and immune dysfunction leads to all diseases of aging as well as cancers.
Original Article: https://anamihalceamdphd.substack.com/p/new-study-shows-significant-impact

Truthful comments that add value to our readers, such as additional information, clarification, validation or worthy rebuttal will be posted. The goal of comments on articles is to gain additional truth.

Comments ()